Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure varies; some feel fine, while others may experience dizziness or fainting. Symptoms differ by individual. In severe cases, low blood pressure can be dangerous and life-threatening. A blood pressure reading lower than 90 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) for the top number (systolic) or 60 mm Hg for the bottom number (diastolic) is considered under low BP. The reasons for low (BP) blood pressure can range from dehydration to more serious health issues. Identifying the cause is crucial in order to determine the appropriate treatment, if needed.
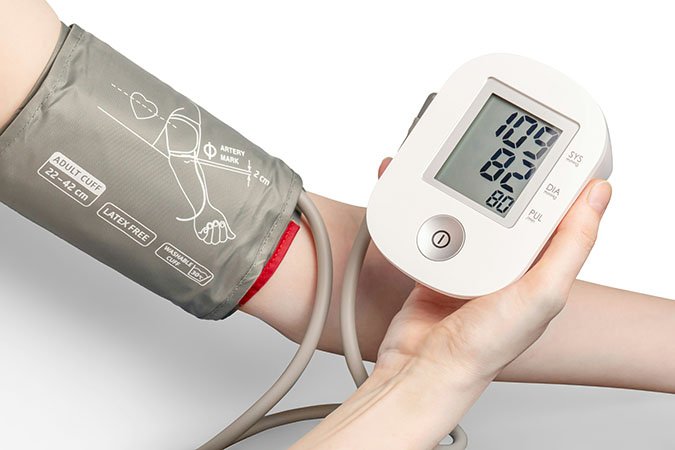
Types of low BP
1.Absolute Hypotension: You have severe hypotension if your blood pressure at rest is lower than 90/60 mm Hg.
2.Orthostatic Hypotension: Orthostatic hypotension occurs when your blood pressure remains low for more than three minutes after standing up from a seated position, with a drop of 20 mm Hg or more in systolic pressure and 10 mm Hg or more in diastolic pressure. It is also known as postural hypotension due to changes in posture.
3.Systolic (Top Number): Systolic blood pressure is the top number in a reading, indicating artery pressure during heartbeats. Normal is below 120 mm Hg; high levels increase risk for heart disease and stroke.
4.Diastolic (Bottom Number): The diastolic number represents the pressure on your arteries when your heart is at rest, between beats
How common it is?
Low blood pressure often goes unnoticed due to no symptoms, making its exact prevalence difficult to determine accurately.. Orthostatic hypotension increases with age, affecting 5% at 50 and over 30% of individuals older than 70. Here we will learn about some reasons for low BP (Blood Pressure).
Symptoms
- Common hypotension symptoms include dizziness, fainting, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, and fast, shallow breathing.
- Other symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, feeling tired or lethargic, confusion, trouble concentrating, and unusual changes in behavior. The effects of hypotension can vary depending on the cause, how quickly it develops, and the individual experiencing it.
- Hypotension occurs more frequently as people age, as slow decreases in blood pressure are normal. Rapid blood pressure drops can cause inadequate blood flow, leading to unpleasant, or even dangerous effects.
- Normally, the body can regulate blood pressure and prevent it from dropping too much. It does this by increasing heart rate or constricting blood vessels to maintain blood flow. However, when the body is unable to compensate for the drop in blood pressure, symptoms of hypotension may occur.
- It’s important to note that many individuals with hypotension may not experience any symptoms at all. In fact, they may be unaware of their low blood pressure unless they measure it themselves.
What are the possible signs of low BP?
- Abnormal heart rate, either too slow or too fast.
- Paler skin tone than usual.
- Cool kneecaps.
- Reduced cardiac output, indicating decreased blood pumping by the heart.
- Decreased urine output.
What are the reasons for low BP?
There are several reasons for low BP. Here are the causes of low blood pressure with brief descriptions:
Reasons for low BP (blood pressure) include dehydration, heart problems, endocrine issues, severe infection, blood loss, and certain medications.
- Dehydration: Insufficient water intake leads to low blood pressure due to decreased fluid in the bloodstream.
- Heart Problems: Conditions like bradycardia, heart attack, or heart failure impair the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively, resulting in low blood pressure.
- Endocrine Issues: Hormone-producing gland problems, such as adrenal insufficiency, disrupt the body’s salt and water balance, leading to low blood pressure.
- Severe Infection (Septicemia): Infections entering the bloodstream cause a drop in blood pressure known as septic shock, which can be life-threatening.
- Blood Loss: Significant blood loss from injury or internal bleeding reduces the blood volume, resulting in low blood pressure.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients like vitamin B12 and folate hinders red blood cell production, leading to low blood pressure.
- Medications: Certain medications, including those for high blood pressure, diuretics, and specific antidepressants, can cause low blood pressure as a side effect.
- Pregnancy: Rapid expansion of the circulatory system during pregnancy can cause a drop in blood pressure, especially in the first 24 weeks.
When to see doctor?
In case you experience symptoms of severe low blood pressure or shock, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical assistance.
Healthcare professionals consider blood pressure too low if it causes symptoms like dizziness or lightheadedness.
If asymptomatic with low blood pressure, your provider may monitor you and suggest keeping a symptom record for evaluation.

Risk Factors
- Hypotension can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status.
- Older adults, especially those over 65, are more likely to experience drops in blood pressure when standing or after eating.
- Certain medications and conditions like Parkinson’s, diabetes, and heart issues can increase the risk of low blood pressure.
Summary
Low blood pressure, or hypotension, can arise from various factors including dehydration, heart issues (like bradycardia and heart attack), endocrine disorders (such as adrenal insufficiency), severe infections (septicemia), significant blood loss, and nutritional deficiencies (e.g., vitamin B12 and folate).
Certain medications, like those for high blood pressure and diuretics, can also cause hypotension. Pregnancy often leads to lower blood pressure due to circulatory system changes.
“Stay connected with us by following our website LifesPotion. Explore more and stay updated with the latest posts.”
